Share this
A Guide to FDM Printale Plastics and 3D Printing Filament
by 3devo on Aug 15, 2015 11:38:00 AM

When it comes to 3D printing, we are witnessing a huge wave of development, either in the 3D printing technology or in the use of innovative printing material. The process of producing 3D prints from various materials is generally called Additive Manufacturing (because the object is produced by adding a number of material layers until finish). In the past years, 3D printing has greatly evolved, featuring several new manufacturing techniques.
Today, engineers and developers strive to improve 3D printing while making use of the latest technologies launched on the market. The current 3D printing technologies are:
- FDM Fused Deposition Modeling
- SLA Stereolithography
- 3DP – Tridimensional Inkjet Printing
- PJP Polyjet printing
- LOM Laminated Object Manufacturing
- DLP Digital Light Processing
- SLS Selective Laser Sintering
Whilst all the above technologies are still under development, each comes with its advantages and disadvantages. The most popular 3D printing method today in terms of affordability, use of technology and 3d print quality is FDM, or Fused Deposition Modeling.

Overview of different 3D printing technologies, via Windesheim
What is FDM?
FDM is a simple, accessible and productive 3D printing technology used for new product development, prototypes and other manufacturing purposes. Since this is an ecological and easy-to-use technology, it is widely used in the transportation and food industry.
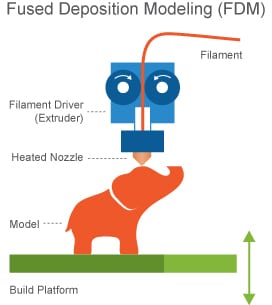
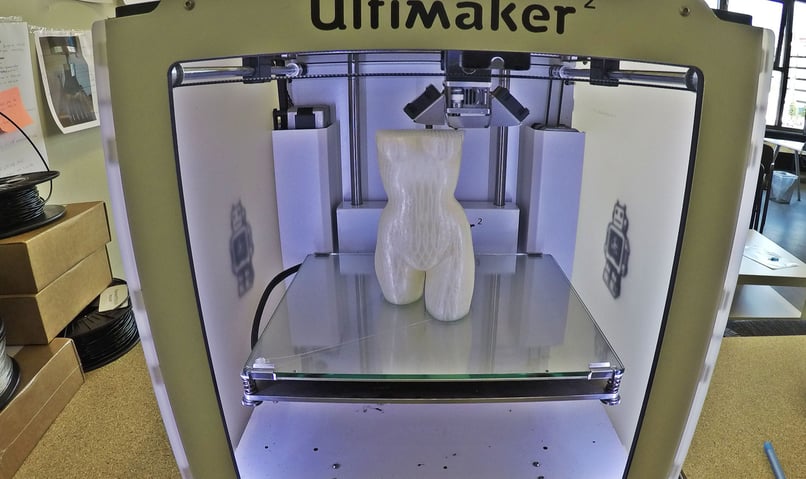
Sideview from a FDM 3D printer, via Printspace3D
How Does it Work?
Specialized software makes possible for the 3D model to be virtually sliced in transversal sections/ layers. The printing technology consists in inserting a plastic filament through an extruder that warms it until to melting. At this point, the melted filament is homogenously applied through extrusion, layer after layer, with high accuracy, in order to manufacture the 3D print according to the CAD pattern.
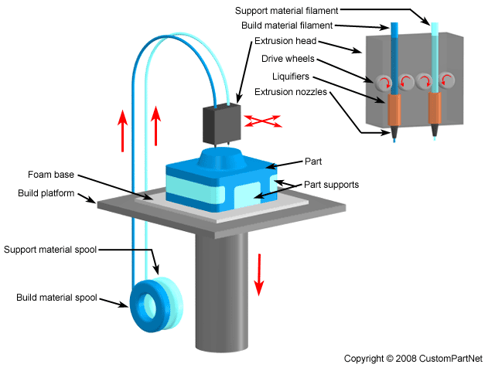
How the FDM process works, via Rapidprototyping
Types of Plastics Used for FDM Production
The prime matter used for the FDM technology consists in plastic materials. However, we are not talking about just any kind of plastics. 3D printing requires a special type of material: thermoplastics. There are countless types of plastic materials used to produce filaments for 3d printing:
- PS (Polystyrene), as a thermoplastic material, can be melted at 100 Celsius degrees. At room temperature it features a glassy state. It can be successfully used for 3D molds with fine details. However, it degrades slow, creating environmental debates.

CD covers are made of PS, via materialrecoveryinc
- BioFila Linen is a relatively new material used for creating 3D printing filament. This material doesn’t in fact contain any linen fibers, but Lignin, an organic material. The properties of BioFila are amazing. The 3D prints feature a texture similar to linen, yet stronger and more porous-looking like structure.

Organic resources are used, via 3ders
- PLA (Polylactic Acid) is a fairly strong material. However, it is less flexible than ABS. what’s interesting about PLA is that it’s biodegradable and will corrode in wet conditions. Since PLA is a resorbable composite, it is widely used in tissue engineering and maxillofacial surgery.

PLA is very appropriate for creating detail, via prototypingengineer
- PA (Polyamide) is used for producing some of the cheapest 3D printing filaments. PA is less brittle than PLA and ABS, thus much stronger. Additionally, it features self-lubricating properties, ideal for gears printing.

PA is tough, stiff and suitable for editing, via alibaba
- PPSF (Polyphenylsulfone) is generally used in product development due to its high heat resistance. In addition, it is appreciated for the increased mechanical strength and resistance to solvents.
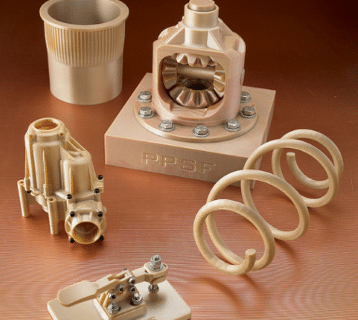
PPSF is a high-performance thermoplastic, via springitalia
- PC (Polycarbonate) is ideal for complex 3D prints, such as fixtures, prototypes or composite works. It features a flexural and high tensile strength.

Some grades of PC are optically transparent, via superdacha
- ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene) is a material that delivers mechanical stability and resistance over time.

The famous Lego bricks are made of ABS, via transvorm
The last three types of plastic materials are the most commonly used for the production of industrial quality filaments. Filaments are an excellent prime matter for professional 3D printers. The better the filament quality, the better the 3D print results. Therefore, it is essential that thermoplastics used for the manufacturing of filaments should feature exceptional properties. The filament quality has a direct impact on the heat and mechanical resistance of the resulted prints. Therefore, PLA and ABS filaments are used to manufacture 3D prints for prototype testing.
What Are The Properties of These Materials?
Thermoplastics are heated, formed and finally cooled in infinite shapes. Such materials feature specific properties that make them indispensable for the 3D printing industry:
- Lightweight (density varies from .9 to 2 gm/cc).
- Resistant to various temperatures: from -100F up to an astonishing 600F.
- Thermal and electrical insulation.
- Adaptable chemistry can turn thermoplastics into objects similar to rubber consistency or as resistant as aluminum.
- Resistant to solvents at room temperature.
- Adding metal fibers or carbon to thermoplastics will confer electrical conductibility.
- Excellent replacements for metal objects, with significant weight savings.
- Resistant on long term and less prone to deformation, unlike metals.
- Engineering thermoplastics feature a tensile strength of over 7,500 psi.

Printing layer by layer, via capinc
Which Industries Rely on 3D Printing and Have Undergone Intense Material Research?
Although 3D printing is a relatively new industry, and there is still no mainstream production method, one thing is sure: the speed of development in the field is absolutely breathtaking. Some of the industries that already use 3D printing technology to improve and stimulate progress are:
- Aerospace industry
- Architecture industry
- Automotive industry
- Commercial products
- Defense industry
- Dental industry
- Consumer electronics
- Education
- Medical industry
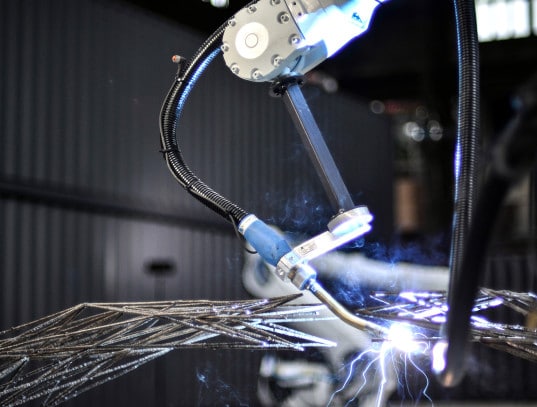

3d printing technology helps MX3D to build a bridge of steel in the center of Amsterdam, via inhabitat
Considering the fact pace of current technologies, industrial techniques and equipment become obsolete very quickly. Whilst many companies are perfectly comfortable to using traditional production methods, many are foreseeing the future and opt for investing their resources to develop using a technology as simple and highly efficient as 3D printing.
Share this
- November 2025 (1)
- October 2025 (1)
- March 2025 (1)
- January 2025 (1)
- December 2024 (2)
- November 2024 (2)
- October 2024 (4)
- September 2024 (2)
- August 2024 (3)
- July 2024 (6)
- June 2024 (3)
- May 2024 (2)
- April 2024 (1)
- March 2024 (1)
- January 2024 (1)
- November 2023 (2)
- October 2023 (5)
- September 2023 (2)
- August 2023 (1)
- July 2023 (1)
- May 2023 (1)
- December 2022 (2)
- June 2022 (1)
- May 2022 (2)
- April 2022 (2)
- March 2022 (6)
- February 2022 (2)
- January 2022 (3)
- December 2021 (3)
- November 2021 (3)
- October 2021 (2)
- September 2021 (3)
- August 2021 (3)
- July 2021 (2)
- June 2021 (1)
- March 2021 (1)
- October 2020 (1)
- June 2020 (1)
- May 2020 (1)
- April 2020 (4)
- November 2019 (1)
- July 2019 (2)
- June 2019 (1)
- May 2019 (1)
- March 2019 (1)
- November 2018 (1)
- September 2018 (1)
- January 2018 (1)
- October 2017 (1)
- September 2017 (1)
- July 2017 (1)
- June 2017 (1)
- May 2017 (1)
- January 2017 (1)
- December 2016 (3)
- November 2016 (2)
- October 2016 (1)
- May 2016 (2)
- August 2015 (2)
- July 2015 (1)