Polymers
Discover the Perfect Materials for Your Innovations with Our Polymer Pyramid and Filament Maker
What is a Polymer?
A polymer is a large molecule composed of repeating units called monomers, akin to a train where each car represents a monomer, and the entire train symbolizes the polymer. These versatile materials are omnipresent, forming the backbone of numerous products, from everyday plastics to the fibers in our clothing.
At 3devo, we empower innovators to unlock the potential of 3D printing by facilitating the transformation of these polymers into novel 3D printing materials. Our expertise in polymers, combined with our Filament Maker, allows you to experiment and develop new filament materials for 3D printing. Let's delve deeper into the Polymer Pyramid to guide you in selecting the best materials for your projects.
%20-%20instasize%20(2).png?width=800&height=640&name=MicrosoftTeams-image%20(39)%20-%20instasize%20(2).png)
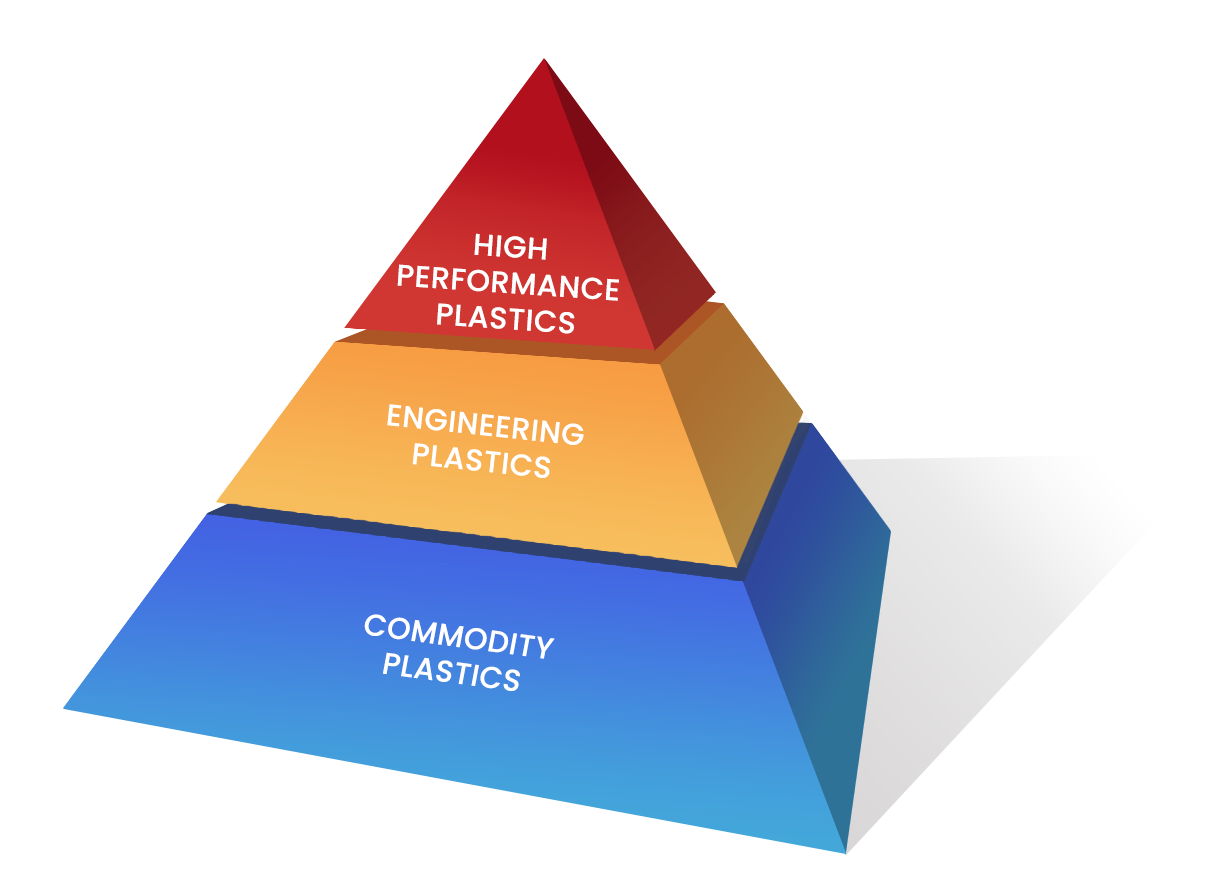
The 3 Tiers of the Polymer Pyramid
The Material Pyramid categorizes plastics into three distinct layers based on their properties and applications, which can be expertly processed using our Filament Maker:
- Commodity Plastics at the base: Commonly used for their cost-effectiveness.
- Engineering Plastics in the middle: Renowned for their enhanced mechanical and thermal properties.
- High-Performance Plastics at the apex: Reserved for specialized applications requiring exceptional durability and resistance.
In industries ranging from manufacturing to prototyping, selecting the right plastic is crucial. The right choice can optimize lead times, reduce structural challenges, enhance manufacturability, and bring unmatched value to a product or innovation. At 3devo, we stand by to assist you in making the right choice, functioning as an integral part of your team.
Commodity Polymers
%20-%20instasize.png?width=800&height=640&name=MicrosoftTeams-image%20(15)%20-%20instasize.png)
%20-%20instasize.png?width=800&height=640&name=MicrosoftTeams-image%20(35)%20-%20instasize.png)
.jpg?width=3264&height=2448&name=MicrosoftTeams-image%20(83).jpg)
%20-%20instasize.png?width=800&height=640&name=MicrosoftTeams-image%20(40)%20-%20instasize.png)
Engineering Polymers
Engineering polymers are versatile materials prized for their flexibility, mechanical strength, chemical stability, and wear resistance. Other notable polymers in this category include PC, POM, and PA12.
%20-%20instasize.png?width=800&height=640&name=MicrosoftTeams-image%20(21)%20-%20instasize.png)
%20-%20instasize.png?width=800&height=640&name=MicrosoftTeams-image%20(32)%20-%20instasize.png)
%20-%20instasize%20(1).png?width=800&height=640&name=MicrosoftTeams-image%20(17)%20-%20instasize%20(1).png)
.jpg?width=3264&height=2448&name=MicrosoftTeams-image%20(81).jpg)
.jpg?width=3264&height=2448&name=MicrosoftTeams-image%20(82).jpg)
.jpg?width=3264&height=2448&name=MicrosoftTeams-image%20(84).jpg)
.jpg?width=3264&height=2448&name=MicrosoftTeams-image%20(85).jpg)
High-Performance Polymers
High-performance polymers have exceptional chemical resistance, thermal stability, and outstanding mechanical properties. Other polymers include PPS, PBI, and PPSU.
%20-%20instasize.png?width=800&height=640&name=MicrosoftTeams-image%20(9)%20-%20instasize.png)
%20-%20instasize.png?width=800&height=640&name=MicrosoftTeams-image%20(26)%20-%20instasize.png)
%20-%20instasize.png?width=800&height=640&name=MicrosoftTeams-image%20(34)%20-%20instasize.png)
%20(1).jpg?width=3264&height=2448&name=MicrosoftTeams-image%20(14)%20(1).jpg)
Explore More Materials with 3devo
Dive deeper into the world of 3D printing materials with 3devo. Apart from the polymers mentioned in the pyramid, we have extensive experience working with a diverse range of materials that can fuel your innovation. Here are some examples:
PE (Polyethylene)
PP (Polypropylene)
HIPS (High Impact Polystyrene)
LDPE (Low-Density Polyethylene)
POM (Polyoxymethylene)
PAHT (High-Temperature Nylon)
ASA (Acrylic Styrene Acrylonitrile)
PSU (Polysulfone)
PA (Polyamide/Nylon)
PHB (Polyhydroxybutyrate)
PAEK (Polyaryletherketone)
PPS (Polyphenylene Sulfide)
FAQ
A polymer is a large molecule made up of repeating units known as monomers. Think of a train where each car is a monomer, and the entire train represents the polymer.
Polymers are integral to modern life, impacting almost every aspect of our daily routines. Polymers are everywhere, from the plastic containers we use to store our food to the fibers in our clothes, shoes, and even the tires on our cars. Their versatile properties – like durability, lightness, and malleability – make them ideal for a myriad of applications. They've revolutionized industries, from healthcare with polymer-based prosthetics and implants to technology with flexible electronic circuits.
Your choice of polymer will depend on factors like the required mechanical and thermal properties, cost considerations, and the specific application of your project. Refer to our Polymer Pyramid and the detailed descriptions of each polymer to guide your selection, or Get in Touch with Us, and we can help you discover the right polymer for your needs.
With our Filament Maker, you have the freedom to experiment and create 3D printing filaments using a wide variety of polymers and materials. Here are some materials that you can use:
-
PLA - A biodegradable material that is easy to work with. Ideal for beginners. Discover the potential of PLA
-
ABS - Known for its strength and durability, it's suitable for creating robust objects. Learn about the properties of ABS
-
PETG - Combines the ease of use of PLA with the strength of ABS, offering a balanced choice for various applications. Explore the versatility of PETG
-
HDPE - A versatile material with good resistance to moisture and chemicals. Understand the applications of HDPE
-
PPSU & PC - High-performance polymers known for their thermal stability and chemical resistance. Dive into the characteristics of PPSU and PC
-
PA12, PAHT, PSU, PVA, ULTEM, PE, PAEK, PPS, PP, ASA - These are other materials that you can experiment with to create filaments with varying properties. Explore the potential of these diverse materials
-
PCL - A biodegradable polyester with a low melting point, making it ideal for prototyping. Learn about the benefits of using PC
-
PEEK & PEKK - These are high-performance polymers with exceptional properties, suitable for advanced applications. Uncover the unique properties of PEEK and PEKK
Feel free to explore and experiment with these materials to create innovative 3D printing filaments. Our team at 3devo is here to assist you in understanding and working with these materials to achieve your project goals.
For further insights, you can dive deeper into the world of polymers and filament-making through our blogs:
- Unlocking Recycling Innovations with 3devo's Solution
- Quick Guide To Polypropylene: With 3D Printing Insight
- How To Start Extruding Carbon Fiber Filament | 3devo
- Correct Settings for Extruding PEEK Filament | 3devo
- How to Recycle PET Plastic into 3D Printing Filament | 3devo
- Extruding Polyphenylene Sulfide on 3devo's Filament Extruder | 3devo
Not all polymers are recyclable. While some, like PLA (Polylactic Acid), are derived from renewable resources and are biodegradable, many others are petroleum-based and can persist in the environment for long periods. It's essential to be informed about the environmental impact of the polymer you're using, considering factors like its source, biodegradability, and recyclability. Learn here to find out more about Which Plastics are Recyclable. Check out more on our mission of providing options for Recycling Filament using recycled plastics.
-
- Quick Guide To Polypropylene: With 3D Printing Insight
- How to Make PEEK Filament - Correct Settings for Extrusion
- The Ultimate Guide to PET Plastic
- Extruding Polyphenylene Sulfide on 3devo's Desktop Filament Extruder
- A Guide to FDM Printable Plastics and 3D Printing Filament
- Testing PAEK - Is It Any Good?
- All You Need to Know About PEKK
- Is PETG The Best Filament in the 3D Printing Industry?
- How To Make Polycarbonate Filament
- Extruding PVA Filament
For a complete list of our material-focused blogs, head over to our blog section.
PLA (Polylactic Acid) is a biodegradable polymer derived from renewable resources like corn starch, making it more environmentally friendly. On the other hand, ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene) is a petroleum-based plastic known for its strength and flexibility but is not biodegradable. Check out our comprehensive guide on the Difference Between ABS and PLA for more guidance.